All target system connections ultimately utilize a variant of the psm /u {user} /a {target} /c {connection_type} executable. Once you have authenticated to PSM through AAM password-less or PVWA credentials, a connection to the target system is launched on PSM through the psm executable. This open connection is then streamed back to the Remote Desktop Manager client, PVWA HTML5 web interface, or an RDP client via the generated RDP file.
The general distinction between the CyberArk types in Remote Desktop Manager is how a user authenticates to PSM and whether the integrated PVWA dashboard is used within Remote Desktop Manager to open a connection rather than directly launching the connection.
These credentials are often linked directly to a connection to facilitate seamless connections to a target system through CyberArk PSM.
CyberArk AAM: Links a user's locally stored private certificate (key) in the user certificate store and the CyberArk CCP REST API service. The certificate thumbprint, linked to an Application (defined in PVWA) that identifies an Remote Desktop Manager client (optionally restricted to specific IP addresses), retrieves the requested credentials from the Digital Vault, optionally managed by the CPM.
CyberArk PVWA: Similar to AAM, but supporting non-AAM authentication methods such as CyberArk (internal authentication), LDAP, Windows (Kerberos integrated authentication), Radius, and SAML (SSO).
CyberArk Dashboard: Provide Remote Desktop Manager users with an alternate interface to PVWA. View a list of Digital Vault Safes and Accounts the currently logged-on user can access. Connect to target systems through the following methods:
Traditional PSM Connection
Bypassing PSM via the Allow connect to host option under Advanced – General. Not recommended.
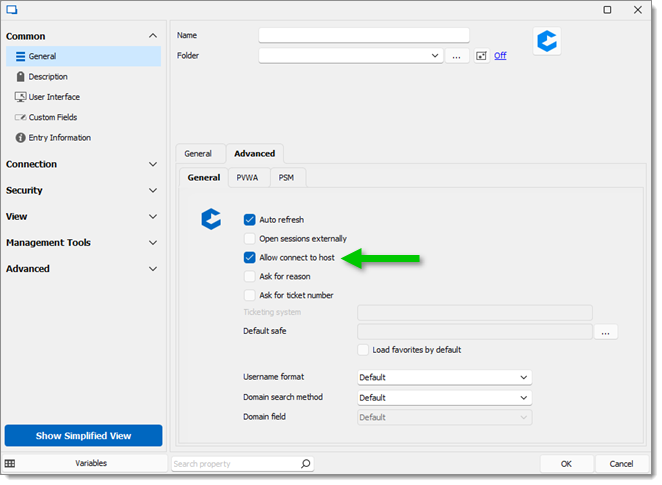
PSM Alternate Shell (also internally known as the Ad-Hoc connection method, different from the Ad-Hoc connection in PVWA). Requires a pre-existing CyberArk PSM Server to be configured.
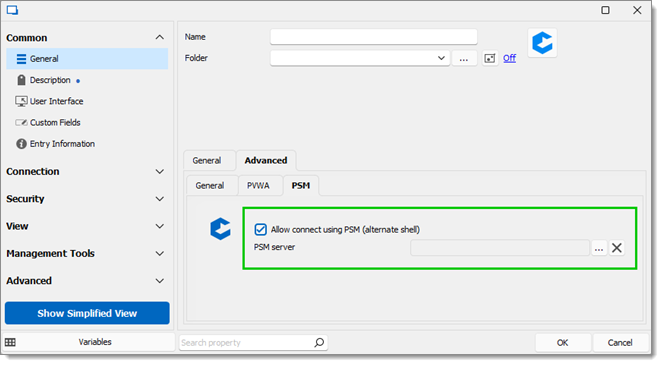
CyberArk PSM Connection - Intended to connect to a specific host using a privileged account and a PSM server connection, leveraging the PSM Alternate Shell connection method.
CyberArk PSM Server - Used with the PSM Connection (and PSM Alternate Shell option of the CyberArk Dashboard connection) to define a PSM server for connecting to a given host.
The CyberArk PVWA credential, CyberArk Dashboard connection, and CyberArk PSM Connection all offer several authentication methods. These authentication methods are to authenticate to PVWA (i.e., if you navigated to the web interface and chose the authentication method), not the target endpoint. Below is how the authentication modes map to the authentication credentials.
The My Account Settings PVWA option is the setting located in File – My Account Settings – CyberArk PVWA. AAM (user vault search) is to find a stored AAM entry within an Advanced Data Source user vault.
CyberArk: Custom, My Account Settings PVWA, AAM (Linked), AAM (user vault search)
LDAP: Custom, My Account Settings PVWA, AAM (Linked), AAM (user vault search)
Radius: Custom, My Account Settings PVWA, AAM (Linked), AAM (user vault search)
Windows: Custom, My Account Settings PVWA, AAM (Linked), AAM (user vault search)
SAML: None
The AAM option offers a drop-down to choose an existing credential.
CyberArk: Custom, AAM
LDAP: Custom, AAM
Radius: Custom, AAM
Windows: Custom, AAM
SAML: None
The AAM option offers a drop-down to choose an existing credential.
AAM: Linked Credential
Custom: Username and Password