The Unix command su, derived from substitute user, grants a user the ability to execute commands with the privileges of another user account.
-
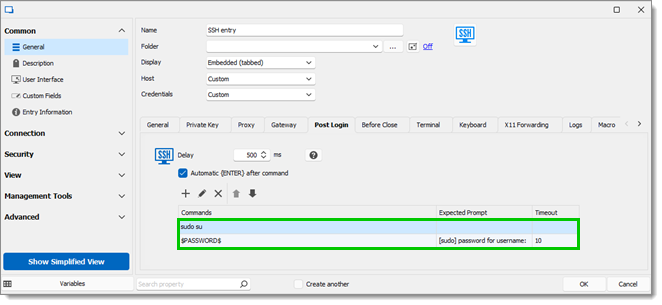
Go to the SSH entry properties in Remote Desktop Manager.
-
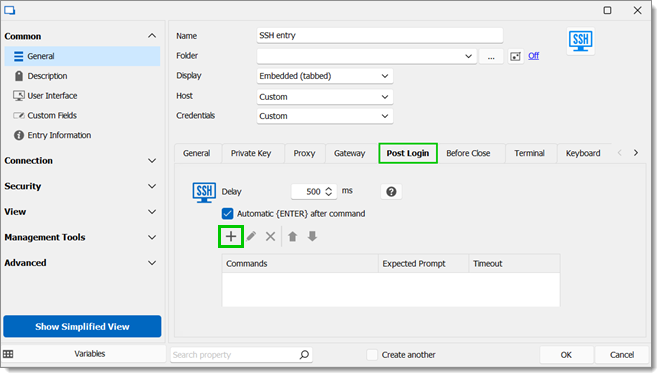
Go to General – Post login and click on the Plus button (New).
Enter sudo su in the Macro Edition window.
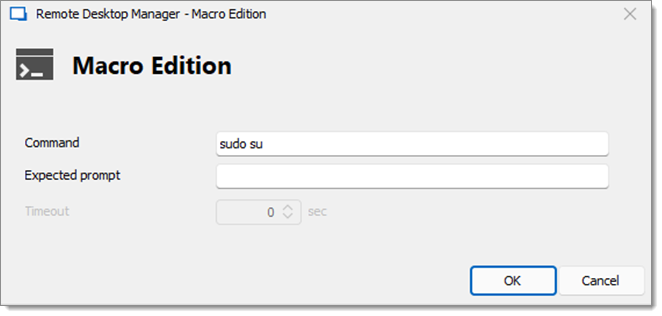
An Expected prompt is not required because we want to execute it as soon as possible.
-
Go back to General – Post login and click on the Plus button (New).
-
Enter the variable $PASSWORD$ and [sudo] password for username: in the Expected prompt (username is used as an example).
-
Select the Timeout.
-
Click OK to close the window.
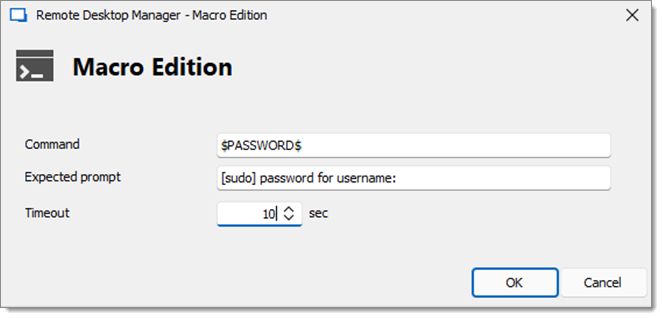
The objective is to ensure the password is sent only when the timing is right with the intended sequence of actions. The terminal awaits the [sudo] password for username: prompt before sending the second command.