Remote Desktop Manager user group based access control allows the creation of a flexible, granular protection system. Flexibility comes at a price, and careful configuration becomes necessary when managing complex systems.
Here are the key points of the user group based access system:
Security is inherited: child items and folders are covered by a parent folder’s security.
Permissions can be overridden: a permission set on a sub folder will override the parent item’s permission.
Permissions are granular: Multiple permissions can be set on entries at once.
While the user group based access control is great to secure access to entries, many other features can be used to add more security layers. For more information, consult the following topics:
Because of the system's great flexibility, it becomes difficult to describe how to achieve the exact security system needed for every possible use case. For this reason, this topic covers the most popular systems currently in use by Devolutions' community members. These strategies can be mixed and matched of course.
See the following for more details:
User groups are mostly used to control user access for multiple users at once. Common user groups types can be:
Service desk: Single point of contact to handle incidents, problems and questions from staff and customers. A service desk provides an interface for activities such as modification requests, software licences, configuration management, and more.
Help Desk: Deparment or person that manages, coordinates and resolves support requests.
Consultants: Usually read-only users employed externally on a temporary basis which can only use a specific subset of entries.
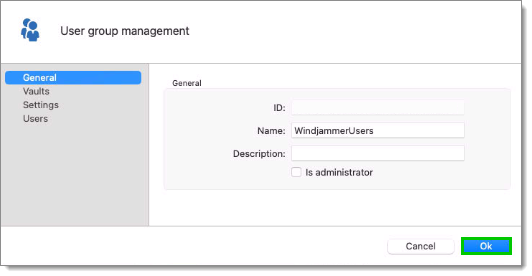
To create user groups, navigate to Administration – User groups, then click Add user groups.
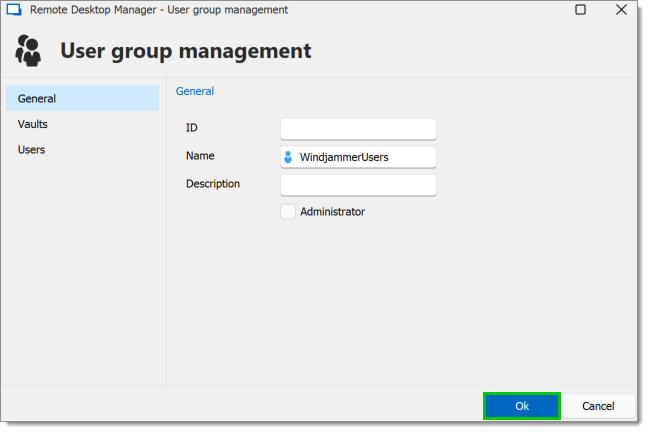
All settings can be left to default unless the user group contains only administrators. In this case, check the Administrator box when configuring the user group. Enter a Name for the user group, then click OK.
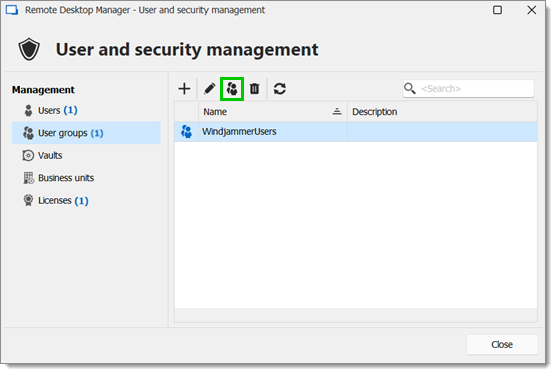
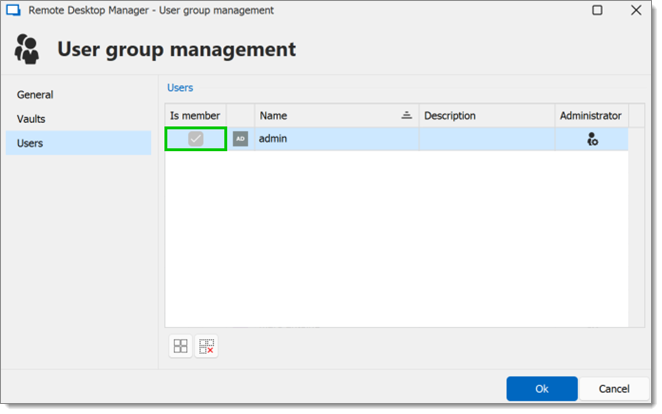
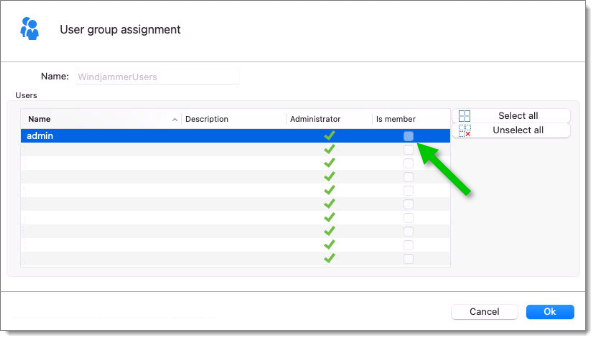
To assign users to the user group, click the Assign user to user group button, then check the Is Member box of the respective user.
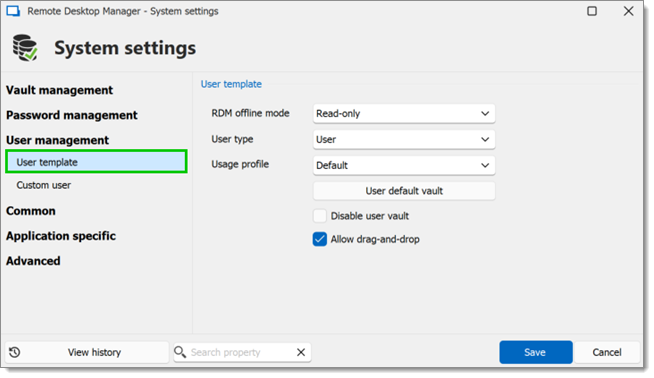
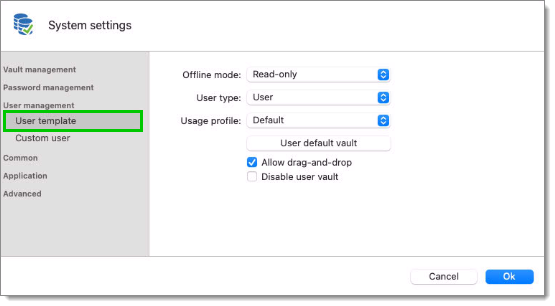
It is also possible to change the default user template. To do so, navigate to Administration – System settings – User management – User template. These settings control the default settings of a new user.
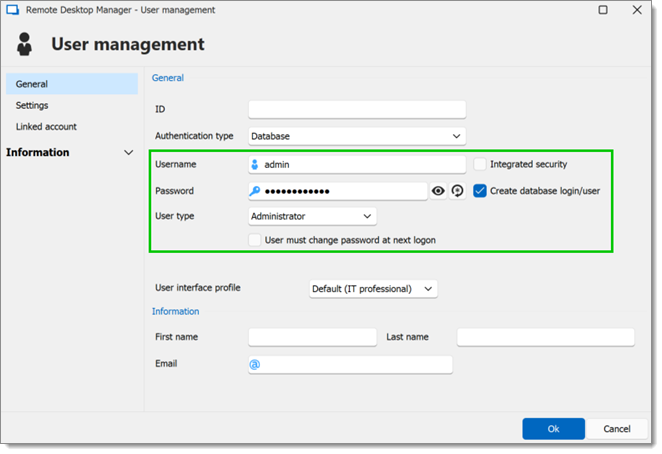
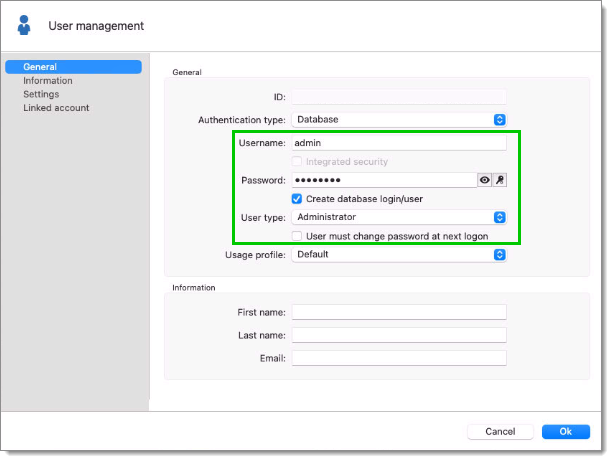
To create users, navigate to Administration – Users, then click Add user. Enter a Login and Password for the user and select the User type.
A user can be assigned to multiple user groups at once by checking the Is member box of the respective user groups in the User groups section of the User management.
Administrators can do everything, regardless of the security. These users are usually the chief officers and senior management.
Restricted users have limited access to resources. They usually have the Add and Edit rights only. These users can be mid or first level executives, such as service desk and help desk.
Users also have limited access to resources much like Restricted users. However, Users have by default the Add, Edit and Delete rights and can perform these actions on all unsecured entries.
Read-only users can only view and use resources, but cannot edit them. These users are usually external consultants.
When creating users, some key points must be taken into consideration:
Should they be able to access any resource without restriction? Then they are meant to be Administrators.
Should they be able to add, edit, or delete entries? A User would have all of these. Alternatively, select specific rights with Restricted user.
Should they be able to see sensitive information, or import and export entries? If not, Read-only users are best used for those who should only have very limited access.
Access is granted or denied to users by setting permissions on entries or folders. Permissions can be given either to individual users or to user groups. It is recommended to grant permissions to user groups to control access for multiple users at once.
To set permissions on an entry, edit any entry, then navigate to the Permissions section. This can also be done when creating the entry.
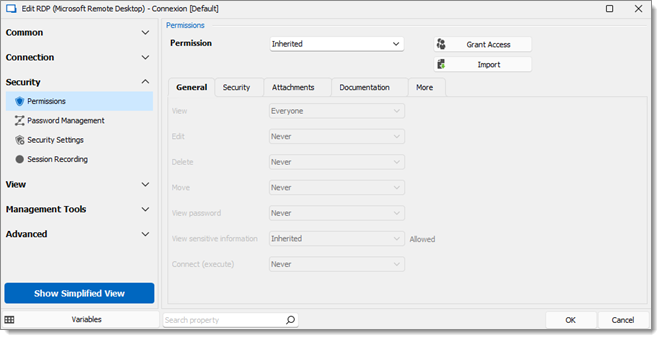
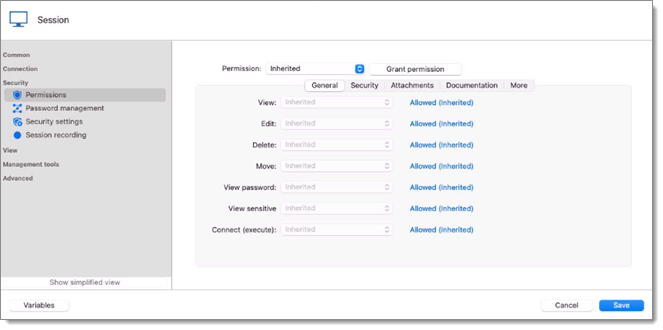
Permissions that are set on folders apply to all child entries. It is considred a best practice to set all the permissions at the vault folder level to Disallowed. As a result, all permissions of all entries are denied by default.
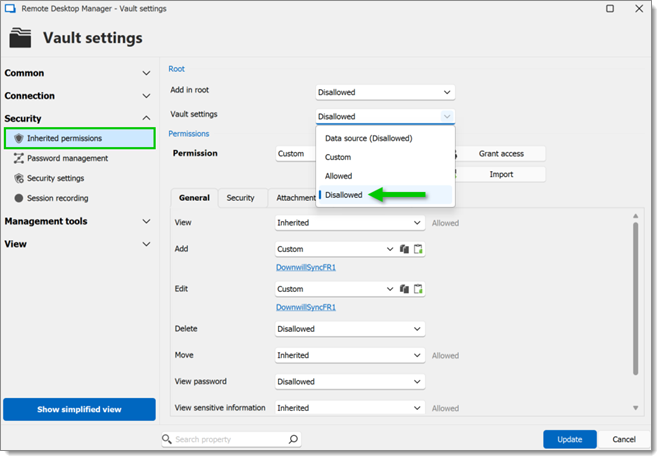
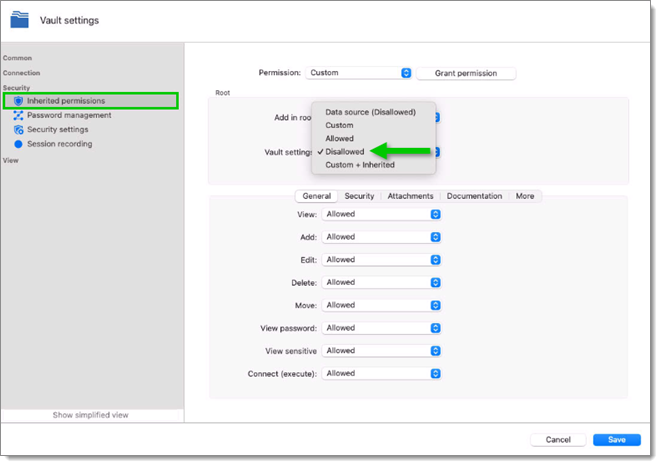
Access is denied to users by expressly granting the access to other users. In other words, all users that are not on the list of a permission have their access denied.
For a user to have access to a sub folder, the user must have at least the view permission on all parent folders.
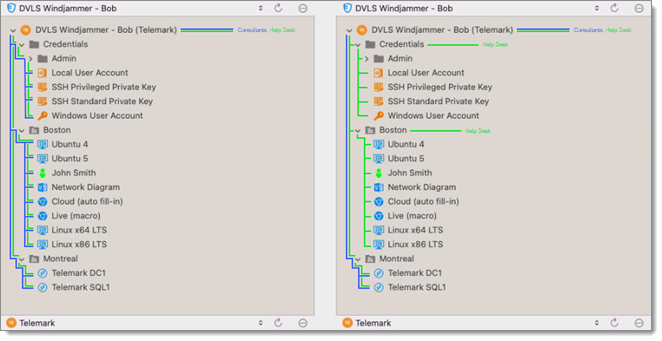
Consider the following structure:
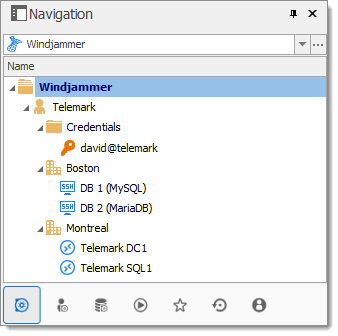
There are three levels of folders: the vault, Telemark, and child items of Telemark.
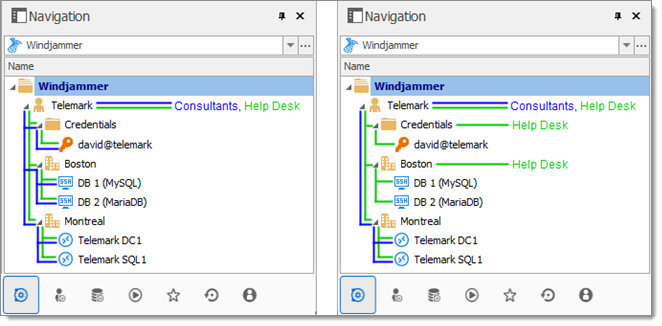
Suppose that a user, such as a consultant, must have access to the Montreal folder only. The consultant must be granted the view permission on the Telemark folder as well. However, granting the view access to the Telemark folder gives to the consultant the permissions to view all child items of Telemark. To deny the view permissions for the consultant on specific child items, the view permissions of these items must be expressly set for other users.
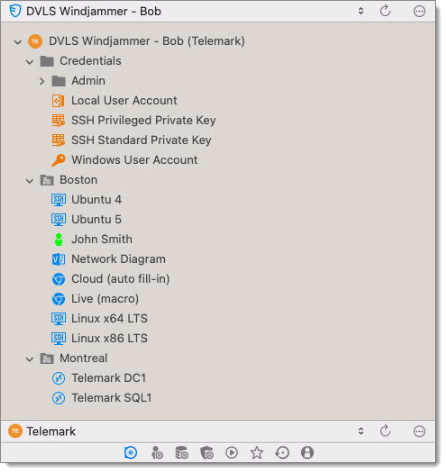
There are three levels of folders: the vault, DVLS Windjammer (Telemark), and child items of DVLS Windjammer (Telemark).
Suppose that a user, such as a consultant, must have access to the Montreal folder only. The consultant must be granted the view permission on the DVLS Windjammer (Telemark) folder as well. However, granting the view access to the DVLS Windjammer (Telemark) folder gives to the consultant the permissions to view all its child items. To deny the view permissions for the consultant on specific child items, the view permissions of these items must be expressly set for other users.