Security Providers exist to encrypt the data at rest (the information stored on the database) using a key shared on every Remote Desktop Manager instance. This way, an attacker would need to compromise the database as well as the security provider to compromise the data.
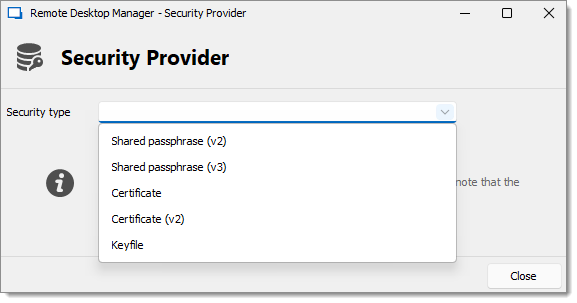
Below is a list of available Security types.
Default: Does not set any security provider.
Shared passphrase: Encrypts the data using a password stored on each Remote Desktop Manager instances. The v3 uses a more secure hashing algorithm than the v2.
Certificate: Encrypts the data using the private key of a certificate installed on each workstation. The v2 uses a more secure encryption algorithm.
Keyfile: Encrypts the data using the a key stored in a file installed on each workstation.
To ensure secure deployment of Remote Desktop Manager with SQL Server on workstations within an organization, it is recommended that an enterprise certificate be used for data encryption. This can be achieved by implementing an Active Directory configuration or using other methods such as a Mobile Device Management (MDM) software.
However, it is important to recognize that when a certificate is exposed to multiple workstations, there is an increased risk that it will be compromised by malicious actors. To mitigate this risk, we recommend using a Devolutions Server that effectively handles encryption at rest while safeguarding the encryption key from Remote Desktop Manager users.
For more detailed information, please refer to Security Model and Encryption (PDF).