The Security dashboard is a tool to offer guidance on how to improve the security of the Remote Desktop Manager platform and also tips on reducing the workload for administrators. Some tips are common infosec best practices, others are a consensus between our owns teams.
The scores are admittedly open to question and we do not pretend each topic has the same relative value for all of our community members. Achieving 100% is surely not an end goal in itself, we simply aim to raise awareness and provide ideas for your own security hardening. 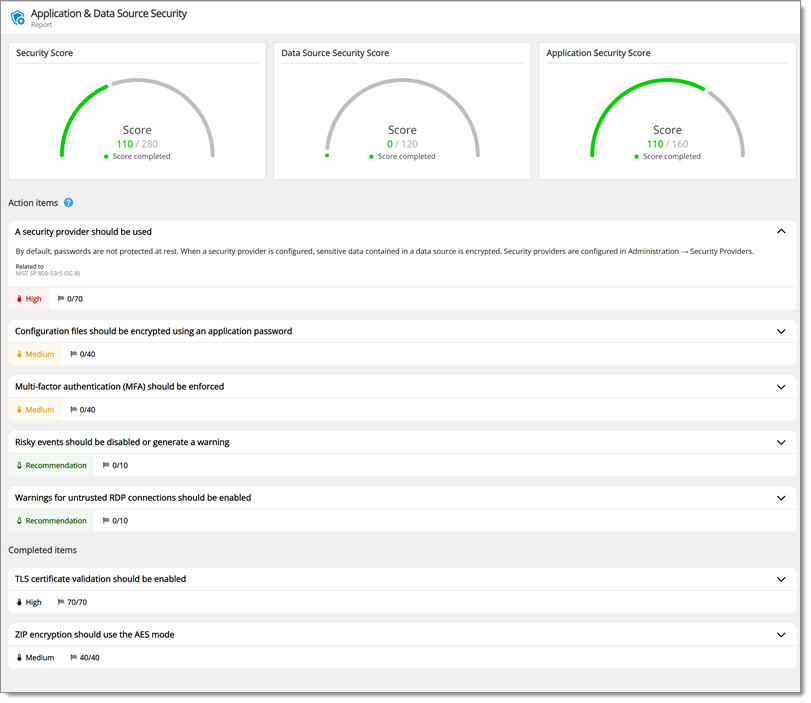
Password policies set requirements for passwords generated with the password generators.
In Administration – Password policies, select Add to create a password policy. Then, the default password policy can be selected in Administration – System settings – Password policy.
By default, passwords are not protected at rest. When a security provider is configured, sensitive data contained in a data source is encrypted.
Security providers are configured in Administration – Security Providers.
Using a master key encrypts sensitive content of XML-based data source files.
The master key can be set under File – Change master key.
Setting a minimal Remote Desktop Manager version is recommended to ensure clients are up to date and have the latest security features.
The application password should be used to encrypt sensitive information in Remote Desktop Manager configuration files.
In File – Settings – Security – Application Security (local), choose Use application password and check Encrypt local files using the application password.
HTTPS is used to protect the communication between the client and the server hosting the data source. Traffic over HTTP is unencrypted and is susceptible to be intercepted and tampered by a malicious third party.
Configure a TLS certificate on the server and set the data source URL to start with https://. See Configure SSL.
Legacy security has been deprecated and will be completely removed starting with version 2023.3 of Remote Desktop Manager.
In Administration – System Settings – Vault Management – Security Settings – Security, disable Use legacy security. See Disable legacy security in Remote Desktop Manager.
Multifactor authentication (MFA) requires an additional mean of authentication when connecting to a data source. This control prevents abuse of compromised, leaked, or weak passwords. The software can be configured to enforce MFA requirements to all users.
In Administration – System Settings – Security Settings, enable Force data source 2-factor configuration.
By default, offline mode is enabled and allows Remote Desktop Manager to automatically cache credentials stored in entries on the client system. This feature should be turned off in high security environments to avoid unnecessary sensitive data exposure.
Some security standards require passwords to be changed at regular intervals. PCI DSS 4.0 requires passwords to be changed every 90 days when the password is the only authentication factor.
Password expiration can be configured in Administration – System Settings – Security Settings – Custom user password expiration (days).
Some entry events can perform powerful actions such as running an external program or script. These events represent a risk if they are modified by a malicious actor. These event types can be disabled if they are not needed, or Remote Desktop Manager can be configured to show a warning when such an event is about to be executed.
In Administration – System Settings – Security Settings, set Risky events to Disabled or Enabled with warnings.
SMS is not recommended for 2FA. A stronger mechanism based on an authenticator application or a physical security key should be used instead.
TLS protects communications between Remote Desktop Manager and the SQL Server instance.
Configure SQL Server to support TLS connections and add encrypt=true to the SQL Server connection.
When this option is enabled, the variable DATA_SOURCE_PASSWORD will resolve to the data source password. This option should be disabled if it is not needed.
In Administration – System Settings – Password Policy, uncheck Allow data source password variable.
Zxcvbn is recommended over the legacy password strength analyzer as it is more reliable.
In Administration – System Settings – Password Policy, set Password strength calculator to Zxcvbn.
Validating certificates guarantees that the connection is established with the intended party and protects against data interception attacks.
In File – Settings – Security – Certificate security, uncheck Ignore application certificate errors.
Transparent data encryption encrypts the database data at rest, which mitigates risks should physical drives or backup tapes be stolen.
Activity logs on the user vault can provide additional information during incident response.
In Administration – System Settings – User vault, check Log user vault activities.
It is preferable to provide rights to users as needed. When enabling this option, vaults will be created with a more limited set of permissions.
In Administration – System Settings – Security, check Create vaults with restricted access by default.
When presented with an unknown certificate, the RDP client should be configured to either present a warning (Warn me) or abort the connection (Do not connect).
In File – Settings – Types – Remote Desktop, set Authentication level to Warn me or Do not connect.
The ZipCrypto algorithm is considered insecure and AES should be used instead. It is susceptible to known-plaintext attacks which can allow recovering the content of the archive without knowing the password (see Why You Should Never Use the NativeZip Crypto in Windows for details on this attack).
In File – Settings – Advanced, uncheck Use ZipCrypto compression (not recommended).