VMware tools make assumptions that their scripts are run in an interactive session and also present warnings the first time that they are run. As it stands today, you have to run commands interactively after you have installed or upgraded their tools.
The PowerCLI configuration has multiple scopes: Session, User, and AllUsers Please refer to their documentation for details and on how to properly configure as per your requirements.
This error message is displayed for various reasons. For a quick diagnostic, launch the VMware vSphere PowerCLI shortcut of the same bitness (64 bit) as your Remote Desktop Manager Some commands will be listed in the table below to diagnose issues in sequence. 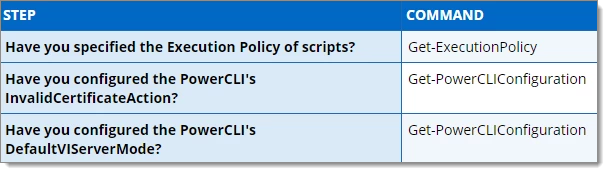
In the PowerShell window: error message appear but it is impossible to read them before the window closes
Remote Desktop Manager ultimately sends a few commands in an encoded script, you can open a PowerShell window and type the following commands sequentially. This way you will have time to see the error messages.
The first command connects with the server, a password prompt will appear:
Connect-VIServer {server ip or name};
The second command lists the virtual machines present on the server. It displays the Name and the ID.
Get-View -ViewType VirtualMachine | select -Property Name, {$_.Moref.Value};
Consult VMware's documentation and make an informed decision as what is the best course of action when you take your security concerns into account. For users that are comfortable in leaving the default certificate on the VMware server, you can launch a PowerShell command window and run the following:
set-PowerCLIConfiguration -invalidCertificateAction "ignore" -confirm:$false
As described in their message, it will be the default value in a coming release. Please consult their documentation and make an informed decision, but most users should accept the Multiple option.
The term 'connect-viserver' is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet, function, script file, or operable program. check the spelling of the name, or if a path was included, verify that the path is correct and try again.
This error occurs because the PowerCLI modules are not linked with PowerShell or the PowerCLI Module for the Connect-ViServer command is missing.
Check is VMware PowerCLI is installed.
Running Get-Module VM* -ListAvailable in PowerShell shows the list of VMware modules installed. 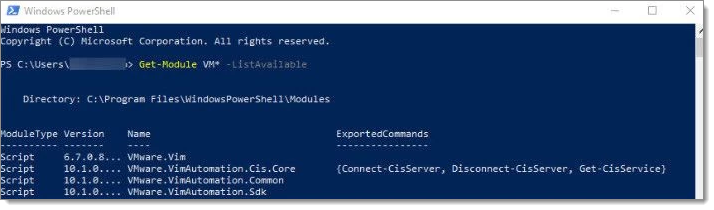 You should see 4 VMware modules listed in PowerShell as shown in the image above.
You should see 4 VMware modules listed in PowerShell as shown in the image above.
You can test to see if PowerShell recognizes the Connect-ViServer command. 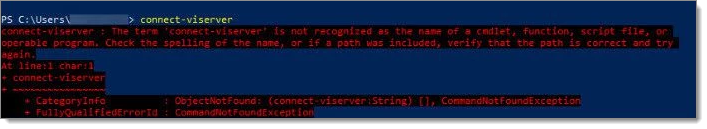 By typing the command, we see that PowerShell does not have the proper module installed.
By typing the command, we see that PowerShell does not have the proper module installed.
In the PowerShell Window, install the PowerCLI modules by using the Install-Module command. Many step by step instructions can be found on Google.
Then type the Get-Module VM* -ListAvailable command again, we can see that the PowerCLI modules are now listed. 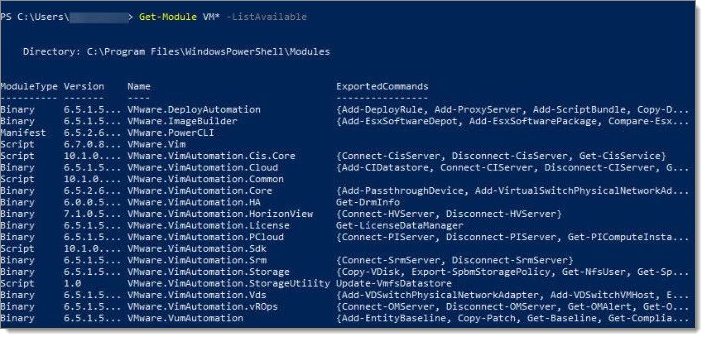 A final test with the Connect-ViServer command, by typing it in PowerShell, the connection is established and the issue should be resolved.
A final test with the Connect-ViServer command, by typing it in PowerShell, the connection is established and the issue should be resolved. 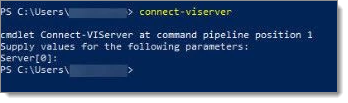
If try on a new computer and have an issue with VimAutomation.Core, you can install it with the command:
Install-Module -Name VMware.VimAutomation.Core -AllowClobber -Scope CurrentUser
After the installation, if you run the command:
Get-Module VM* -ListAvailable
You should get the output below: 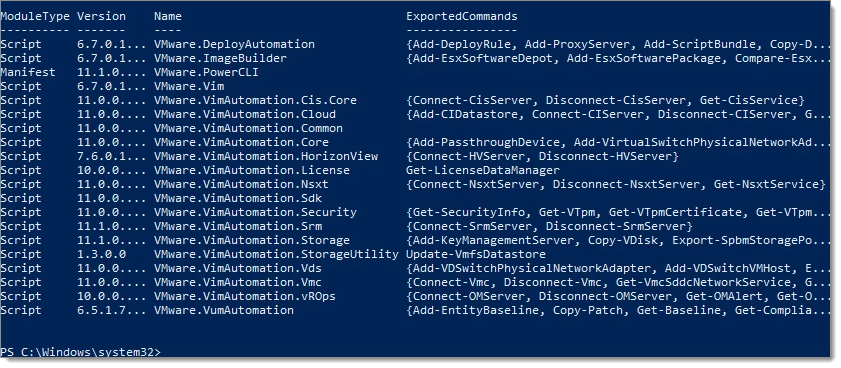 If you restart Remote Desktop Manager with the current user (not running as admin) and open the VMware Dashboard entry, after 30 seconds, you should see all your servers.
If you restart Remote Desktop Manager with the current user (not running as admin) and open the VMware Dashboard entry, after 30 seconds, you should see all your servers.
If this does not work, create a PowerShell entry, the blue one, select Embedded Script and type the script below:
Import-Module VMware.PowerCLI;
Connect-ViServer "SERVER_IP";
Get-View -ViewType VirtualMachine | select -Property Name, {$_.Moref.Value};
Click OK twice and try to start the Powershell entry.
If you get an error about execution policies, please refer to https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/module/microsoft.powershell.core/about/about_execution_policies?view=powershell-5.1
But you can resolve the issue with the following command;
Set-ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted -Scope CurrentUser
Please refer to your administrator to ensure this command is allowed to be used within your infrastructure.