SSH tunneling is used to create an encrypted connection over an untrusted network. It consists of an encrypted tunnel leveraging SSH protocol, and thus providing a secure connection for data transfer. The SSH tunnel can be used to establish a kind of virtual private network (VPN) to access services across firewalls.
This is the procedure to establish a basic SSH tunnel to reach a remote machine:
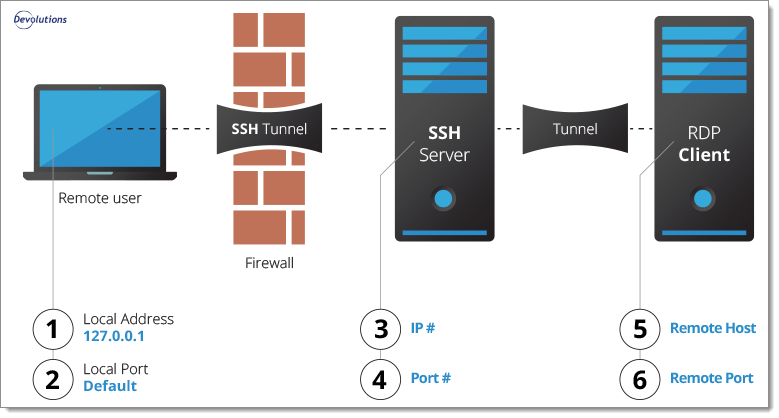
To create an SSH tunnel, local connections through a specified port must be forwarded to an SSH server. For SSH tunnels, a given port of one machine needs to be forwarded to a port on the other machine which will be the other end of the tunnel. Once the SSH tunnel has been established, the user can connect to earlier specified port at first machine to access the network service.
Create an SSH tunnel entry (New entry – Session – SSH tunnel).
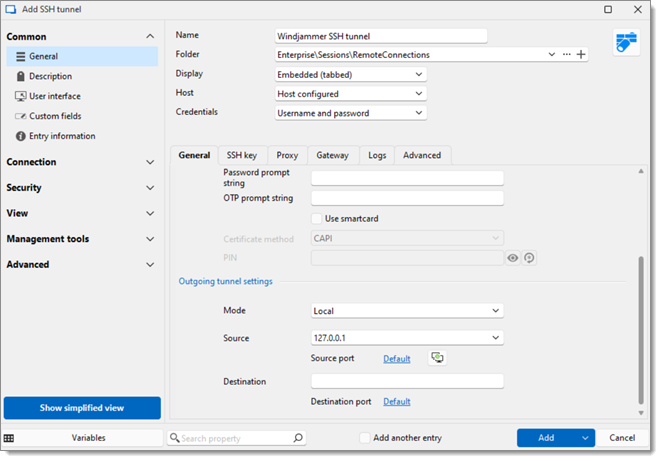
Set up the properties as follows:
| SETTINGS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Host | Set the IP address of the SSH server. |
| Port | Set the port of the SSH server. The default port is 22. |
| Set public key | Set up the public key. |
| Username | Enter the username used to connect to the SSH server. |
| Password | Enter the password used to connect to the SSH server. |
| SETTINGS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Mode | Select between:
|
| Source | The local address must be left to 127.0.0.1. |
| Source port | In most cases leave the local port to its default value 3390. |
| Remote host | Enter the host or IP address of the remote client. |
| Remote port | Set the final port to be reached, in most cases it is best to leave it to its default value of 3389. |
At this time, launch the entry to check if the tunnel successfully opens or not, then end the session.
Create an RDP session entry and fill in the required settings before clicking on Add:
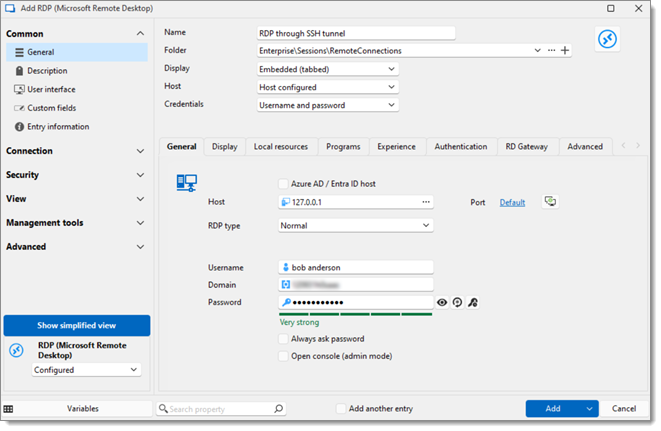
| SETTINGS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Host | Enter the local address which is 127.0.0.1. |
| Port | Enter the local port, which is 3390. |
| RDP type | Leave the RDP type to Normal. |
| Username | Enter the username of the remote host. |
| Domain | Enter the domain of the remote host. |
| Password | Enter the password of the remote host. |
In the VPN/Tunnel/Gateway section of the RDP session, select set the Connect field to Always connect, and the Type field to SSH link.
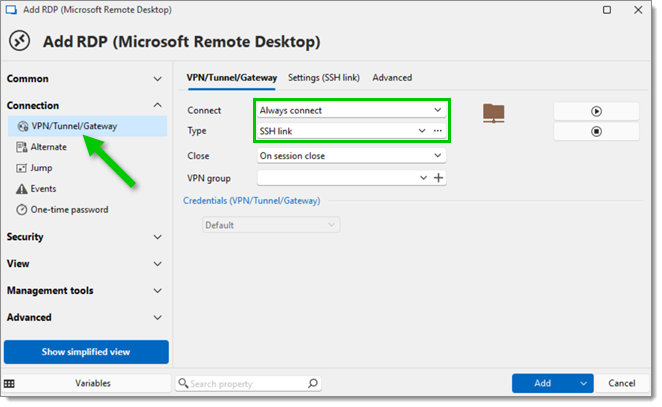
Still in the VPN/Tunne/Gateway section, go to the Settings (SSH link) tab, and select the newly created SSH tunnel entry from the Session dropdown menu. Click on Add.
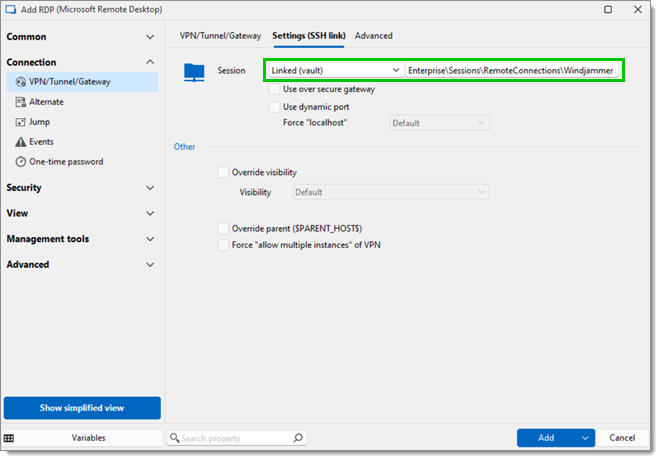
The session is now configured with the following instructions: for each connection that comes on the source 127.0.0.1 and port 3390, forward that connection to the SSH server and request the server to forward that connection to the remote host.