Remote Desktop Manager has integrated support for the Microsoft Remote Desktop Client (MSRDC), providing enhanced options for RDP connections alongside the classic Microsoft Terminal Services Client (MSTSC).
See the full blog article: Remote Desktop Manager now supports MSRDC: enhanced RDP client options.
MSTSC: Classic RDP client, pre-installed with Windows.
MSRDC: Modern RDP client, primarily for Azure Virtual Desktop, available as a separate download.
MSTSC: Includes a GUI for connection configuration.
MSRDC: Lacks a GUI, relying on RDP files for connections, making it more suited for integration with tools like Remote Desktop Manager.
MSTSC: Distributed and updated via Windows Update, with longer support cycles.
MSRDC: Faster release cycles, can be downgraded if needed, not officially supported outside Azure Virtual Desktop.
Enhanced features: MSRDC supports features like server-side resolution changes and desktop resizing.
Flexibility: Faster updates and the ability to revert to previous versions if needed.
Bug fixes: Common RDP bugs may be resolved quicker in MSRDC.
Ensure MSRDC is installed on your system since it is not included with Remote Desktop Manager. It is also possible to deploy MSRDC on several computers with automatic updates instead of manually.
In Remote Desktop Manager, select an RDP entry and click on Properties.
In the General section, select the Advanced tab. From there, set the RDP version to MSRDC.
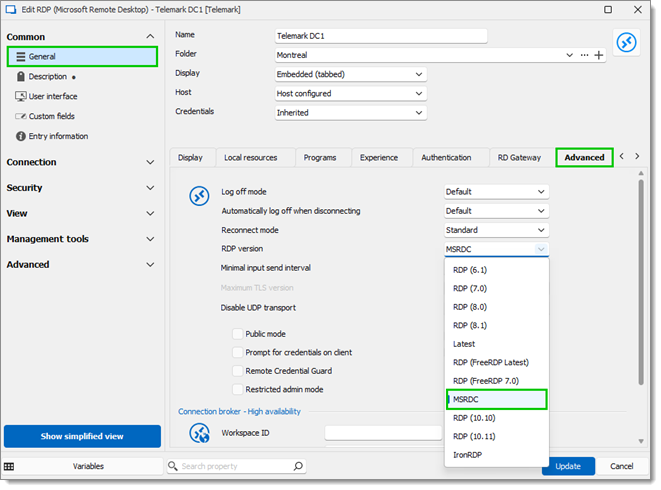
Click Update to save your changes.
While MSTSC remains the default choice for many due to its built-in nature and simplicity, MSRDC offers advanced features and quicker updates, making it a valuable alternative within Remote Desktop Manager. For issues related to MSTSC, MSRDC provides a useful comparison tool and potential solution.