The SQL authentication will be enabled after the migration. It will however not be possible to create users with that authentication type. The goal is only to support the migration and it is advised to disable the SQL authentication once all users are migrated.
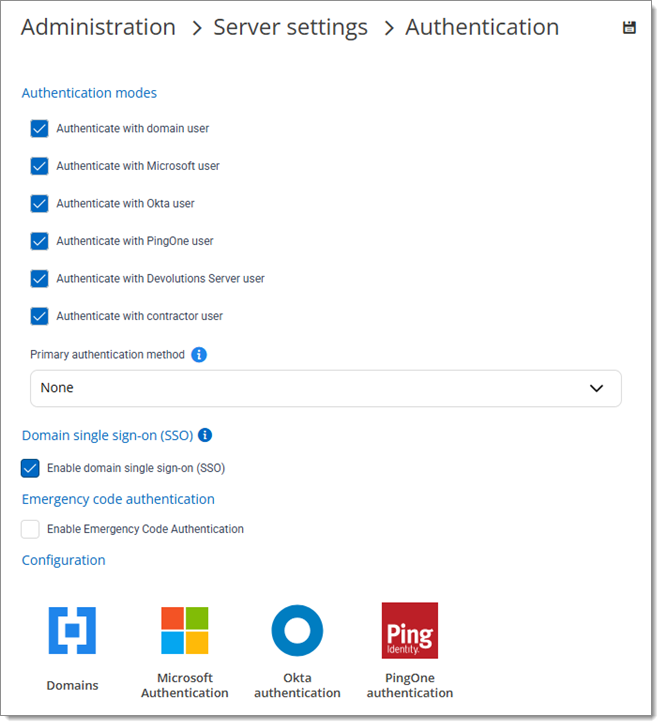
The Authentication section allows the administrator to select which authentication types can be used to connect on Devolutions Server.
The machine hosting Devolutions Server must be joined to the configured domain for Windows Authentication to work.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Authenticate with domain user | The domain is used to authenticate the user. |
| Authenticate with Microsoft user | AzureAD is used to authenticate the user. |
| Authenticate with Okta user | Okta is used to authenticate the user. |
| Authenticate with PingOne user | PingOne is used to authenticate the user. |
| Authenticate with Devolutions Server user | The Devolutions Server is used to authenticate the user. You must create the initial user through the Devolutions Server Console. |
| Authenticate with contractor user | Allow authentication with a contractor user, i.e., a temporary user with limited access rights and UI options. |
| Primary authentication method | By selecting a primary authentication method, users who do not already have a personalized choice of authentication type for the login page will be automatically directed to the chosen method. |
| Domain single sign-on (SSO) | Domain single sign-on (SSO) requires further configuration on your IIS server. |
| Enable Emergency Code authentication | The application will send an email that contains an emergency code to authenticate if any of the above authentication methods are not working. The Email setting is required for this option to work. |
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Domain | Configure the Domain type. |
| Microsoft Authentication | Configure the Office365 type. |
| Okta Authentication | Configure the Okta type. |
| PingOne Authentication | Configure the PingOne type. |
| Authentication migration | Migrate the authentication method of the existing user account to another authentication method or another domain in Active Directory or Azure Active Directory. |