To use Integrated Authentication (Windows Authentication) on macOS, you will need to setup a Kerberos ticket linking your current user to a Windows domain account. A summary of key steps are included below.
This experimental feature has worked in our internal tests and is a workaround to the integrated security feature which does not work on macOS with SQL Server.
That being said, the initial implementation of Kerberos was meant to help our community with using this authentication method. However, multiple changes have been made on the Kerberos side since the implementation, so it is possible that this method is now outdated.
We offer two methods, the manual discovery or a PowerShell Script
Run on: Windows PC that is joined to your Active Directory Domain. Note that any production grade domain will have more than one domain controller. Either of the following methods could answer with a different server depending on a multitude of factors. Be prepared to run this discovery again if the designated server becomes unavailable.
nltest.exe is a console utility that you can run using the basic command interpreter or PowerShell.
Run nltest in the command shell of your choice.
nltest /dsgetdc:%USERDNSDOMAIN%
DC: \\dc-33.domain.company.com
Address: \\2111:4444:2111:33:1111:ecff:ffff:3333
The command completed successfully
Copy the DC name which is the required KDC configuration value, in this case dc-33.domain.company.com
Run the following in a PowerShell window (remember that the PC must be joined to the target domain)
$dcinfo = Get-ADDomainController -Discover
Write-Output "Domain name $($dcinfo.Domain)"
Write-Output "Domain Controller $($dcinfo.HostName)"
Write-Output "`nSuggested krb5.conf content`n-----------------------------------------"
Write-Output "[libdefaults]"
Write-Output "default_realm = $($dcinfo.Domain.ToUpper())"
Write-Output "
Write-Output "[realms]`n$($dcinfo.Domain.ToUpper()) = {"
Write-Output "kds = $($dcinfo.HostName)"
Write-Output "}"
Edit the /etc/krb5.conf in an editor of your choice, note that you need to elevate your privileges (sudo or other). If you have obtained the result of the PowerShell script, simply copy the appropriate lines. Follows the steps needed if you used the manual discovery.
The domain must be in ALL CAPS
Configure the following settings:
[libdefaults]
default_realm = DOMAIN.COMPANY.COM
[realms]
DOMAIN.COMPANY.COM = {
kdc = dc-33.domain.company.com
}
Then save the krb5.conf file and exit.
Use the command kinit username@DOMAIN.COMPANY.COM to get a TGT from KDC. You will be prompted for your domain password.
kinit username<area>@DOMAIN.COMPANY.COM
Use klist to see the available tickets. If the kinit was successful, you should see a ticket.
klist
krbtgt/DOMAIN.COMPANY.COM@ DOMAIN.COMPANY.COM.
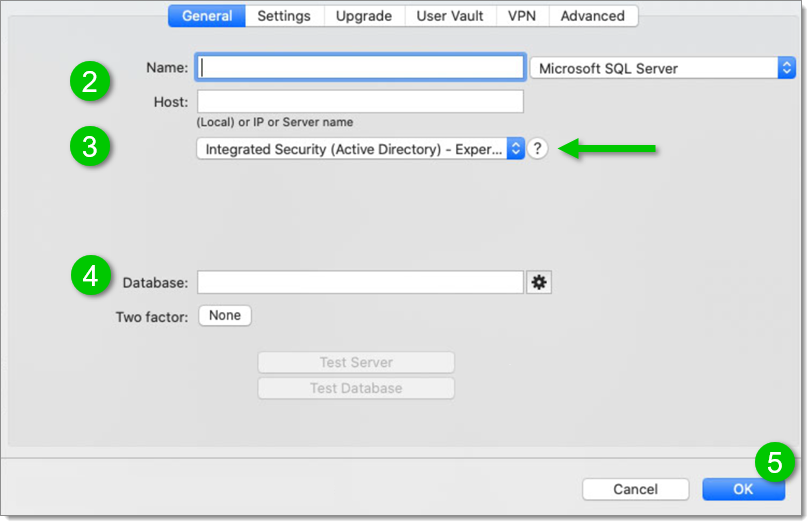
Create a new SQL Server data source.
Fill in the data source information (Name and Host).
Select the “ Integrated Security (Active Directory) – Experimental ” mode.
Select the database.
Save the data source.
If you have followed all the steps above, you should be able to connect successfully to the data source.